Resistance Colour Code Chart: Complete Guide by Origin-IC
In every electronic circuit, resistors play a critical role in controlling current flow, dividing voltage, and ensuring safe operation of other components. Because resistors are usually small and cylindrical, it is not practical to print their resistance values in numbers. To solve this, manufacturers developed a standard system using coloured bands to represent the resistance value, tolerance, and sometimes temperature coefficient. This system is known as the Resistance Colour Code Chart.
Understanding the resistance colour code chart is one of the most basic and important skills in electronics. It helps you quickly identify the resistance value of a resistor just by looking at it. In this detailed article, Origin-IC explains everything you need to know about the resistance colour code chart, how to read it, and why it matters in modern electronics.
What Is a Resistance Colour Code Chart?
A resistance colour code chart is a visual reference table that shows what each colour on a resistor’s body represents. Each colour corresponds to a number, a multiplier, and sometimes a tolerance or temperature coefficient.
Do you want to visit Char Dham? Char Dham Travel Agent is the best place to plan your Char Dham tour. You can book the tour from here.
The colour code follows the IEC 60062 international standard, which means the system is universally accepted across the electronics industry. Whether you are working with resistors in Asia, Europe, or the USA, the same colours have the same meanings.
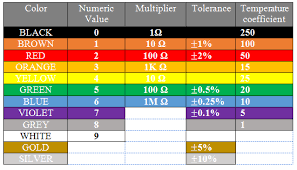
The Standard Resistance Colour Code Chart
Here is the complete resistance colour code chart used to identify resistor values:
| Colour | Digit | Multiplier | Tolerance | Temperature Coefficient (ppm/°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black | 0 | ×1 | — | — |
| Brown | 1 | ×10 | ±1% | 100 |
| Red | 2 | ×100 | ±2% | 50 |
| Orange | 3 | ×1,000 | — | 15 |
| Yellow | 4 | ×10,000 | — | 25 |
| Green | 5 | ×100,000 | ±0.5% | — |
| Blue | 6 | ×1,000,000 | ±0.25% | 10 |
| Violet | 7 | ×10,000,000 | ±0.1% | 5 |
| Gray | 8 | ×100,000,000 | ±0.05% | — |
| White | 9 | ×1,000,000,000 | — | — |
| Gold | — | ×0.1 | ±5% | — |
| Silver | — | ×0.01 | ±10% | — |
| None | — | — | ±20% | — |
This chart serves as a universal guide for decoding the colour bands on all resistors, whether they are 4-band, 5-band, or 6-band types.
Would you like to visit Indiar? A tour operator in India is the best place to plan your tour. You can book a tour from here.
How to Use the Resistance Colour Code Chart
To read a resistor using the resistance colour code chart, follow these steps:
- Identify the Tolerance Band:
The tolerance band (usually gold, silver, or no colour) is slightly separated from the others. Start reading the bands from the opposite end. - Refer to the Chart:
Each colour corresponds to a digit. Match the colours on the resistor to their values in the chart. - Apply the Multiplier:
Multiply the digits by the multiplier value given by the third (or fourth) band. - Add Tolerance:
The last band gives you the tolerance, which defines how much the actual resistance may vary from the stated value.
Example 1: Reading a 4-Band Resistor
Suppose a resistor has the following colour bands: Brown, Black, Red, Gold.
- Brown = 1 (First digit)
- Black = 0 (Second digit)
- Red = ×100 (Multiplier)
- Gold = ±5% (Tolerance)
Resistance = 10 × 100 = 1,000 ohms (1kΩ) ±5%.
Would you like to visit Haridwar? Travel agents in Haridwar are the best place to plan your trip. You can book your tour right here.
That means the actual resistance value lies between 950Ω and 1,050Ω.
Example 2: Reading a 5-Band Resistor
Now, if the resistor has Brown, Green, Black, Red, Brown, then:
- Brown = 1
- Green = 5
- Black = 0
- Red = ×100
- Brown = ±1%
Resistance = 150 × 100 = 15,000 ohms (15kΩ) ±1%.
This higher accuracy resistor is often used in precision circuits.
Example 3: Reading a 6-Band Resistor
For Brown, Black, Black, Red, Brown, Red, the meaning is:
- 1, 0, 0 → Significant digits
- Multiplier = ×100
- Tolerance = ±1%
- Temperature Coefficient = 50 ppm/°C
Resistance = 100 × 100 = 10,000 ohms (10kΩ) ±1%.
This resistor is highly stable and ideal for temperature-sensitive circuits.
Understanding Tolerance
Tolerance is a crucial aspect of resistor performance. It indicates how much the actual resistance can vary from the stated value.
- ±1% or ±2%: High-precision resistors
- ±5%: Standard resistors for general use
- ±10% or ±20%: Low-cost resistors for non-critical circuits
For example, a 220Ω resistor with ±10% tolerance can have an actual resistance between 198Ω and 242Ω.
Temperature Coefficient
In 6-band resistors, the last band indicates how the resistance changes with temperature. The value is given in ppm/°C (parts per million per degree Celsius).
For instance, a resistor with a coefficient of 50 ppm/°C means the resistance changes by 0.005% per degree Celsius.
This factor becomes important in precision instruments, measurement devices, and temperature-sensitive systems.
Mnemonic for Remembering the Colour Code
A simple way to memorize the order of colours is through a mnemonic.
Here’s an easy one to remember:
“Black Brown Red, Orange Yellow Green, Blue Violet Gray White.”
Each word represents a colour in order from 0 to 9. Once you memorize this sequence, reading resistors becomes much faster and easier.
Common Mistakes When Using the Resistance Colour Code Chart
- Reading the Wrong Direction:
Always start from the end opposite the tolerance band. - Confusing Similar Colours:
Red, orange, and brown can look similar, especially in poor lighting. - Ignoring Tolerance:
Tolerance affects precision; always consider it in calculations. - Faded or Dirty Bands:
Old resistors may have discoloured bands; verify with a multimeter.
Why the Resistance Colour Code Chart Is Important
- Quick Identification:
It allows technicians and engineers to instantly determine resistor values without tools. - Universal Standard:
The same colour meanings are recognized worldwide. - Space Efficiency:
Perfect for tiny resistors where numerical printing isn’t possible. - Error Reduction:
Helps prevent incorrect resistor placement during manufacturing or repair.
Applications of Resistors
Resistors are used in nearly every type of electronic circuit, including:
- LED Circuits: To limit current and prevent burnout.
- Amplifiers: For setting bias levels and controlling gain.
- Filters: To create specific frequency responses.
- Microcontrollers: For pull-up or pull-down configurations.
- Voltage Dividers: To produce reference voltages.
Without resistors, electronic devices would not function safely or accurately.
Origin-IC: Trusted Source for Precision Resistors
At Origin-IC, we take pride in delivering high-quality, precision resistors that comply with international standards. Our resistors are designed for reliability, accuracy, and long-lasting performance in all conditions.
We understand that precision matters in electronics — a small error in resistance can cause large deviations in output. That’s why Origin-IC ensures every resistor undergoes rigorous quality control and testing.
Whether you’re designing complex circuits or building educational projects, Origin-IC offers components that provide consistent and dependable performance.
Beyond manufacturing, we also believe in educating the next generation of engineers and hobbyists. Resources like this guide help make complex electronic concepts simple and practical.
Conclusion
The resistance colour code chart is a universal and efficient method to identify resistor values quickly and accurately. By understanding what each colour represents, you can easily decode any resistor’s value, tolerance, and stability just by looking at its colour bands.
From simple LED circuits to high-end instrumentation, resistors are the backbone of every electrical design. Mastering the colour code chart allows you to work confidently, save time, and prevent costly mistakes.
At Origin-IC, we stand by precision, quality, and reliability — the same principles that make the resistance colour code chart a timeless standard in electronics.
| Follow ODG: |
| YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@Origin_Data |
| Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/OriginDataGlobalLimited |
| Twitter: https://twitter.com/Origin_IC |
| Tiktok: https://www.tiktok.com/@origin_data |
| Szxlxc: https://www.szxlxc.com |