Exploring the Role of 3D Modeling in Modern Millwork Shop Drawings
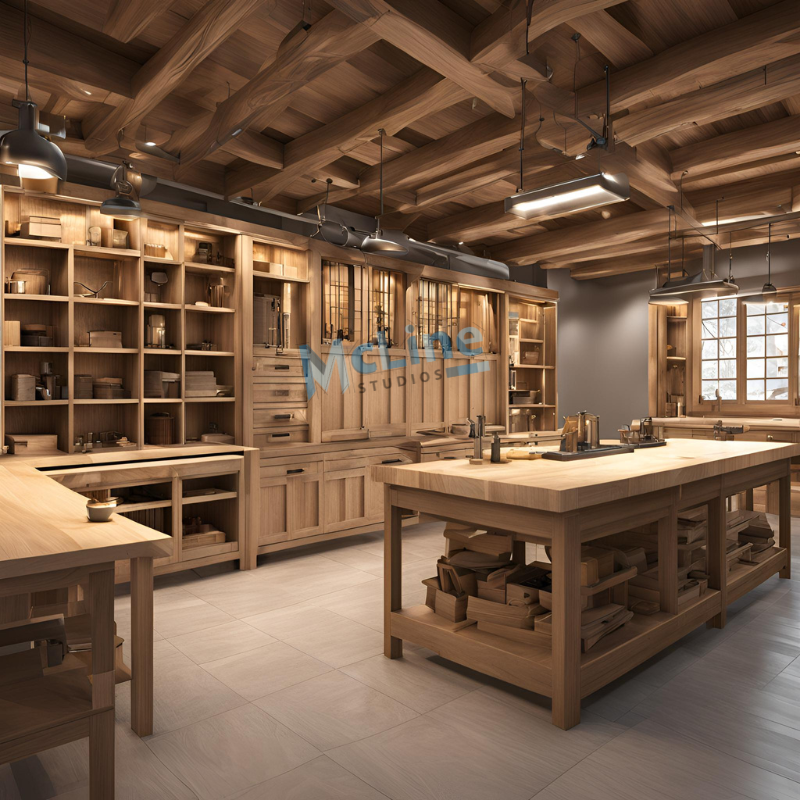
In the ever-evolving construction and design industries, precision and clarity are paramount. Millwork shop drawings, which serve as blueprints for intricate custom woodwork, are critical in transforming creative ideas into tangible structures.
Traditionally reliant on 2D drafting, millwork has experienced a seismic shift with the adoption of 3D modeling technologies. This transformation has redefined how designers, fabricators, and contractors approach projects, bringing a new level of accuracy and visualization.
3D modeling allows for creating detailed, lifelike representations of millwork components, providing stakeholders with a comprehensive view of design intent before a single piece of material is cut.
Do you want to visit Char Dham? Char Dham Travel Agent is the best place to plan your Char Dham tour. You can book the tour from here.
Beyond visual appeal, it improves communication, reduces errors, and accelerates production timelines. This blog delves into the ways 3D modeling enhances millwork shop drawings, the tools driving this shift, and why it has become indispensable in modern construction workflows.
What Are Millwork Shop Drawings?
Millwork shop drawings are detailed plans used in the construction and design of custom woodwork, cabinetry, and other architectural features. These drawings serve as a roadmap for transforming design concepts into real, functional products. They focus on specifics such as dimensions, materials, finishes, and joinery, providing clear instructions for manufacturing and installation.
These drawings are essential in projects like cabinetry, furniture, decorative moldings, and wall paneling. Unlike general blueprints, millwork shop drawings zoom in on the finer details, ensuring that every piece fits perfectly and aligns with the design vision.
Would you like to visit Indiar? A tour operator in India is the best place to plan your tour. You can book a tour from here.
For example, if you’re creating custom kitchen cabinets, the millwork shop drawings will include precise measurements, the type of wood to be used, finish options, and even how the cabinets will be assembled and installed.
The drawings also act as a communication tool between architects, designers, manufacturers, and installers. They help avoid misunderstandings and reduce errors during production. This makes the entire process smoother, saving time and money.
In short, millwork shop drawings bridge the gap between ideas and execution. Whether it’s for a small residential project or a large commercial interior, these drawings are a crucial part of ensuring the final product matches the design perfectly.
Would you like to visit Haridwar? Travel agents in Haridwar are the best place to plan your trip. You can book your tour right here.
The Basics of 3D Modeling
3D modeling is the process of creating a digital representation of an object or surface in three dimensions. This is widely used in industries like architecture, gaming, film, engineering, and product design. At its core, 3D modeling allows designers to bring ideas to life by crafting virtual objects that look realistic and can be viewed from any angle.
The process starts with choosing the right software. Popular tools include SketchUp, Blender, Autodesk Maya, and 3ds Max. Beginners often start with user-friendly programs like SketchUp or TinkerCAD before moving to more advanced software.
The basic building blocks of 3D models are polygons, which are flat shapes like triangles or squares. These polygons are connected to form the surface of an object. The smoother the object, the more polygons are used. For example, a simple cube has six flat sides, but a sphere will require many tiny polygons to look round.
There are different techniques in 3D modeling. Common ones include box modeling, where you start with a simple shape like a cube and refine it, and sculpting, where you “carve” and shape the model as if working with digital clay.
Once the model is created, it can be textured and colored to look realistic. Lighting and rendering are added to give the final model depth and detail.
With practice, anyone can learn 3D modeling and use it to create everything from simple objects to complex scenes. It’s a skill that combines creativity and technical knowledge.
Advantages of Using 3D Modeling in Millwork Shop Drawings
3D modeling has become a game-changer in creating millwork shop drawings. Unlike traditional 2D drawings, 3D models provide a realistic and detailed view of the design. This makes it easier for designers, manufacturers, and clients to visualize the final product before it is built.
One of the key advantages of 3D modeling is improved accuracy. By working in three dimensions, it’s easier to ensure that all parts fit together correctly. This reduces errors and rework during manufacturing. The model also highlights any potential clashes or design issues early in the process, saving time and money.
Another benefit is better communication. 3D models are easy to understand, even for people who don’t have a technical background. Clients can see exactly how their cabinets, furniture, or other millwork items will look in their space. This clarity helps in getting faster approvals and making confident decisions.
3D modeling also supports faster revisions. If changes are needed, they can be made quickly without redoing the entire drawing. The updated model can then be used to automatically generate updated shop drawings and material lists.
Finally, 3D modeling helps streamline manufacturing processes. Many advanced software programs can create CNC-ready files directly from the 3D model. This ensures precision and speeds up production.
In summary, 3D modeling enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and improves collaboration, making it an essential tool for modern millwork drafting.
Challenges in Adopting 3D Modeling for Millwork
3D modeling is transforming how millwork projects are designed and executed. However, adopting this technology comes with challenges that can make the transition from traditional methods difficult.
One major challenge is training and expertise. 3D modeling software can be complex, and learning to use it effectively takes time and practice. Many millwork professionals, accustomed to 2D drawings, may need to learn entirely new skills, which could slow down projects initially.
Another issue is cost. High-quality 3D modeling software and the hardware required to run it can be expensive. Small millwork firms or independent designers may struggle to justify these upfront investments.
Compatibility issues are also common. Millwork projects often involve collaboration with architects, contractors, and other trades. If these stakeholders use different software or tools, sharing and integrating 3D models can become a challenge.
Moreover, time constraints can be a barrier. While 3D modeling offers long-term efficiency, creating detailed models can take more time upfront compared to traditional drafting. This could delay projects, especially if clients are not aware of the added benefits.
Lastly, there’s resistance to change. Many professionals are hesitant to move away from methods they have used successfully for years. The fear of disrupting existing workflows can make the shift to 3D modeling feel overwhelming.
Despite these challenges, the advantages of 3D modeling—such as better visualization, improved accuracy, and enhanced collaboration—make it a worthwhile investment for the future of millwork.
The End Note
The integration of 3D modeling into millwork shop drawings represents a significant leap forward in the construction and design industries. By offering enhanced visualization, improved accuracy, and streamlined collaboration, 3D modeling bridges the gap between design intent and manufacturing execution.
While the transition from traditional 2D methods poses challenges such as training, costs, and resistance to change, the long-term benefits far outweigh the initial hurdles.
As technology continues to evolve, 3D modeling is set to become an indispensable tool in millwork drafting, enabling professionals to deliver higher-quality results, reduce errors, and foster better communication among stakeholders.
Embracing this innovation not only future-proofs workflows but also ensures that the intricate artistry of millwork is translated seamlessly from concept to reality.