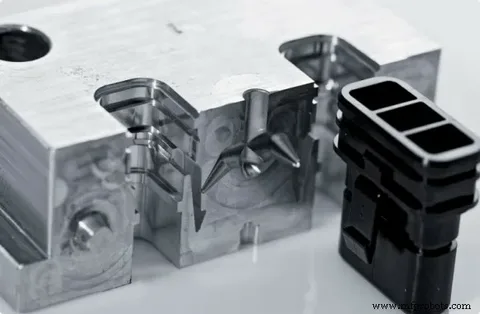
Choosing Between Injection Molding and Rapid Prototyping for Low-Volume Production
When businesses are looking to produce products in low volumes, choosing the right manufacturing method is crucial. Two popular techniques for low-volume production are injection molding and rapid prototyping. Both methods offer distinct advantages depending on the project’s needs. In this article, we will compare Injection Molding vs Rapid Prototyping to help you understand which method best suits your low-volume production requirements.
Understanding Injection Molding
Injection molding is a widely-used manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold to produce parts. This technique is especially valuable for creating complex geometries and high-precision products. The process typically starts with the design of a mold, which can be quite expensive but pays off in large-scale production due to its efficiency.
For low-volume production, injection molding can be both advantageous and challenging. While the initial investment in creating the mold is high, the production costs per unit drop significantly as the volume increases. However, for volumes on the lower end, the mold cost might not be justifiable unless the design is optimized for rapid, efficient production. Thus, when deciding between injection molding vs rapid prototyping, businesses need to weigh the cost of tooling against the unit price and potential order quantities.
Do you want to visit Char Dham? Char Dham Travel Agent is the best place to plan your Char Dham tour. You can book the tour from here.
The Benefits of Injection Molding for Low-Volume Production
Despite the high upfront costs, injection molding offers a variety of benefits, especially for low-volume production. Once the mold is created, each part can be produced rapidly, offering a high level of consistency and quality. The process can be used for a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, and composites, making it versatile for different product types.
Another advantage of injection molding is its scalability. While initially designed for high-volume production, the method can be suitable for small batches when a product requires durability, strength, or precision. For industries like automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods, where product integrity and material performance are crucial, injection molding can provide a reliable solution even at low production volumes.
Exploring Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process that builds parts layer by layer using a 3D printer or similar technology. This method has gained significant popularity for its ability to quickly produce prototypes and functional parts without the need for expensive molds. Rapid prototyping is especially useful when design iterations or testing are required before full-scale production begins.
Would you like to visit Indiar? A tour operator in India is the best place to plan your tour. You can book a tour from here.
Rapid prototyping offers the ability to produce complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible with traditional manufacturing methods, including injection molding. Additionally, the absence of tooling costs makes it an appealing option for companies with low-volume production needs. This method can accommodate frequent design changes and can be an ideal solution for industries looking to test products before committing to mass production. When comparing injection molding vs rapid prototyping, rapid prototyping stands out for its flexibility in design and speed of production.
Advantages of Rapid Prototyping for Low-Volume Production
For low-volume production, rapid prototyping offers numerous advantages over traditional manufacturing techniques. One of the most significant benefits is its speed. Since there is no need for mold creation or long setup times, products can be produced and tested in a fraction of the time it would take with injection molding. This allows companies to respond quickly to market demands or design changes.
In addition to speed, rapid prototyping allows for greater design freedom. Since the parts are created layer by layer, it’s easier to integrate intricate features and internal structures that would be challenging to achieve with injection molding. For industries like aerospace, healthcare, and consumer electronics, where innovation and precision are essential, rapid prototyping offers a distinct advantage. Furthermore, the relatively low cost of producing prototypes means that businesses can explore different design concepts without significant financial risk.
Would you like to visit Haridwar? Travel agents in Haridwar are the best place to plan your trip. You can book your tour right here.
Injection Molding vs Rapid Prototyping: Making the Right Choice for Low-Volume Production
When it comes to choosing between injection molding vs rapid prototyping for low-volume production, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. The best choice depends on several factors, including the complexity of the product, the desired material, production timelines, and budget constraints.
For projects that require high strength, durability, and precision, injection molding may be the better choice despite the higher initial costs. This method is ideal for parts that will undergo significant wear and tear or need to meet stringent industry standards. On the other hand, if the primary goal is speed, flexibility, and the ability to make design changes quickly, rapid prototyping offers distinct advantages. It’s especially valuable when low-volume production runs are needed with frequent revisions or testing. Understanding the unique needs of your project will help you determine whether injection molding or rapid prototyping is the optimal choice for your low-volume production goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both injection molding and rapid prototyping have their respective advantages for low-volume production. Injection molding is a cost-effective solution when precision and durability are critical, while rapid prototyping excels in flexibility, speed, and ease of iteration. By carefully considering your project’s requirements, you can make an informed decision on which method—Injection Molding vs Rapid Prototyping—will deliver the best results for your low-volume production needs.