Optimizing Data Storage with RAID Controller Cards: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to RAID Controller Cards
As data storage needs increase in the modern world of IT hardware, the demand for reliable, efficient, and secure solutions continues to grow. One of the most crucial components in storage optimization and management is the RAID Controller Card. This device ensures that data stored across multiple drives is managed effectively, enhancing both performance and data protection.
In this post, we’ll explore what RAID Controller Cards are, how they function, their benefits in computer hardware, and why they play such a vital role in data-intensive environments. We’ll also discuss their use in the broader context of storage devices and technology.
What is a RAID Controller Card?
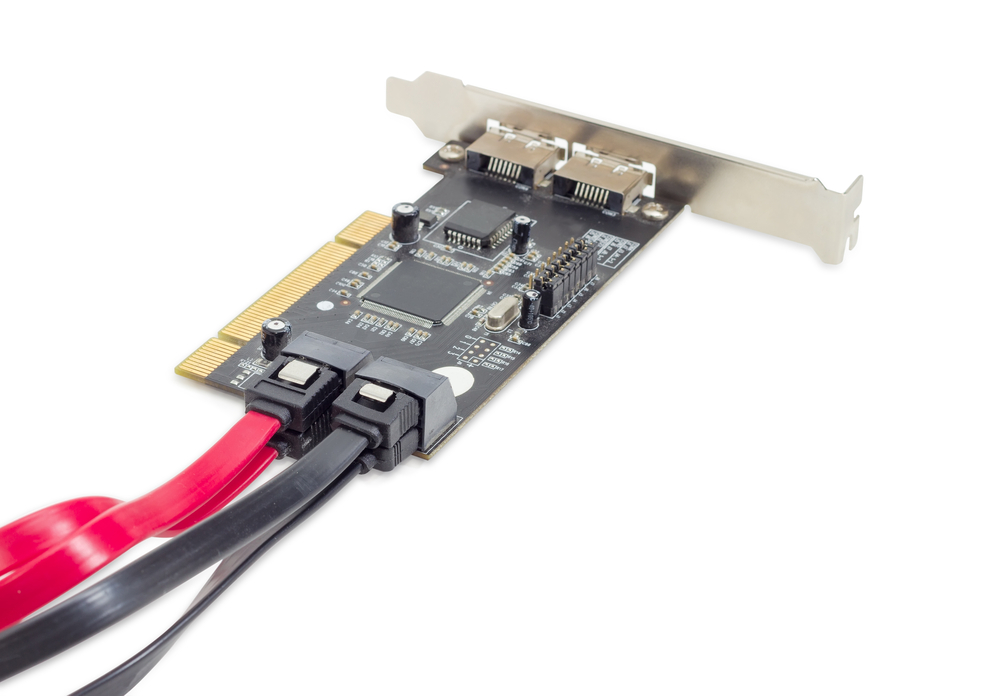
A RAID Controller Card (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a hardware device used to manage multiple hard drives or solid-state drives in a RAID configuration. It allows multiple storage devices to work together to improve performance, enhance data redundancy, and ensure better fault tolerance. RAID controllers can be implemented as a dedicated hardware card or through software built into the system.
Do you want to visit Char Dham? Char Dham Travel Agent is the best place to plan your Char Dham tour. You can book the tour from here.
There are various RAID levels—such as RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10, and more—that offer different combinations of performance and redundancy. Each level of RAID brings its own unique set of features, balancing between faster data access, increased storage efficiency, and improved data protection.
Types of RAID Levels
Understanding the various RAID levels helps users make better choices based on their specific storage needs:
- RAID 0
RAID 0 stripes data across multiple drives, which significantly increases read and write speeds. However, it offers no redundancy. If one drive fails, all data is lost. RAID 0 is ideal for scenarios where performance is prioritized over data safety, such as for video editing or gaming. - RAID 1
RAID 1 mirrors data between two or more drives, providing excellent redundancy. If one drive fails, the system can continue to operate using the mirrored drive, making RAID 1 suitable for environments where data integrity is crucial, like financial systems or small business networks. - RAID 5
RAID 5 offers both improved performance and redundancy. It stripes data across several drives while also storing parity information, which can be used to rebuild data in the event of a drive failure. RAID 5 is commonly used in business settings where a balance between performance and data protection is needed. - RAID 10
RAID 10, a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1, provides both speed and redundancy by mirroring and striping data. It requires a minimum of four drives and is ideal for high-performance and high-availability environments, such as database servers.
How a RAID Controller Card Works
A RAID Controller Card manages the interaction between the system and the Storage Devices configured in a RAID array. By controlling how data is distributed across multiple storage devices, the card optimizes read and write operations. The controller also handles data redundancy, which is essential for preventing data loss in case of drive failure.
Would you like to visit Indiar? A tour operator in India is the best place to plan your tour. You can book a tour from here.
The RAID Controller Card functions as a mediator between the CPU and the hard drives or SSDs, allowing for efficient data storage and retrieval. For higher RAID levels like RAID 5 or RAID 10, the controller also calculates parity and ensures that mirrored data is properly managed, ensuring that data remains intact even in the event of hardware failures.
Benefits of RAID Controller Cards in IT Hardware
RAID Controller Cards offer numerous advantages, making them an essential part of IT hardware in various settings:
1. Enhanced Data Protection
One of the key benefits of RAID configurations, especially with RAID levels like RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 10, is the ability to protect data through redundancy. In the event of a drive failure, data remains secure and accessible.
Would you like to visit Haridwar? Travel agents in Haridwar are the best place to plan your trip. You can book your tour right here.
2. Improved Performance
RAID arrays, particularly those managed by RAID Controller Cards, improve system performance. Striping data across multiple drives increases read and write speeds, making RAID controllers ideal for businesses or users who work with large volumes of data or need high-speed access.
3. Cost-Effective Storage Solution
RAID allows multiple storage drives to function as a single unit, reducing the need for more expensive single large-capacity drives. With a RAID Controller Card, organizations can utilize multiple smaller, more affordable drives while still achieving the desired level of performance and data protection.
4. Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance is another vital benefit of RAID controllers. Depending on the RAID level, if one or more drives fail, the RAID Controller Card ensures that the system continues to function while the faulty drive is replaced and the data is rebuilt.
5. Scalability
As businesses grow, so do their data storage needs. RAID Controller Cards allow for easy scalability by letting users add more storage drives to the RAID array, ensuring seamless system performance even as storage requirements increase.
RAID Controller Cards in the Context of Storage Devices and Technology
The evolving landscape of computer hardware and technology has brought significant advancements in storage devices, including the development of RAID Controller Cards that are faster, more reliable, and capable of handling larger volumes of data. As storage technologies advance, RAID continues to be an essential part of many business and personal data management strategies.
Storage devices such as SSDs, HDDs, and even hybrid drives benefit from RAID technology, especially in high-performance computing environments. RAID Controller Cards ensure that these devices are optimized for both speed and reliability, which is essential for tasks that involve large-scale data processing.
How to Choose the Right RAID Controller Card
Choosing the right RAID Controller Card depends on several factors, including your performance requirements, budget, and data protection needs. Here are a few things to consider when selecting a RAID controller:
- Supported RAID Levels
Ensure the controller supports the RAID level that best meets your needs. For instance, RAID 1 or RAID 5 for redundancy or RAID 0 for pure performance. - Number of Drives
Consider how many drives the RAID controller supports. If you plan on scaling up your storage solution, opt for a card that can handle multiple drives. - Interface Type
RAID controllers come with different interface types such as SATA or SAS. Make sure the card is compatible with your existing storage devices and system architecture. - Hardware vs. Software RAID
Hardware RAID controllers provide better performance but come at a higher cost. Software RAID is a more affordable option but may require more processing power from the CPU.
Conclusion
In conclusion, RAID Controller Cards are essential components in managing storage devices, particularly in data-intensive environments. They offer several benefits, including enhanced data protection, improved performance, cost efficiency, fault tolerance, and scalability. Whether you’re setting up a home office or managing an enterprise data center, a RAID Controller Card is a critical tool in ensuring your data is safe and accessible.
With advancements in IT hardware, the importance of RAID Technology continues to grow. As businesses and individuals handle increasing amounts of data, RAID configurations will remain vital to optimizing data storage systems, and RAID Controller Cards will continue to be the backbone of these systems.