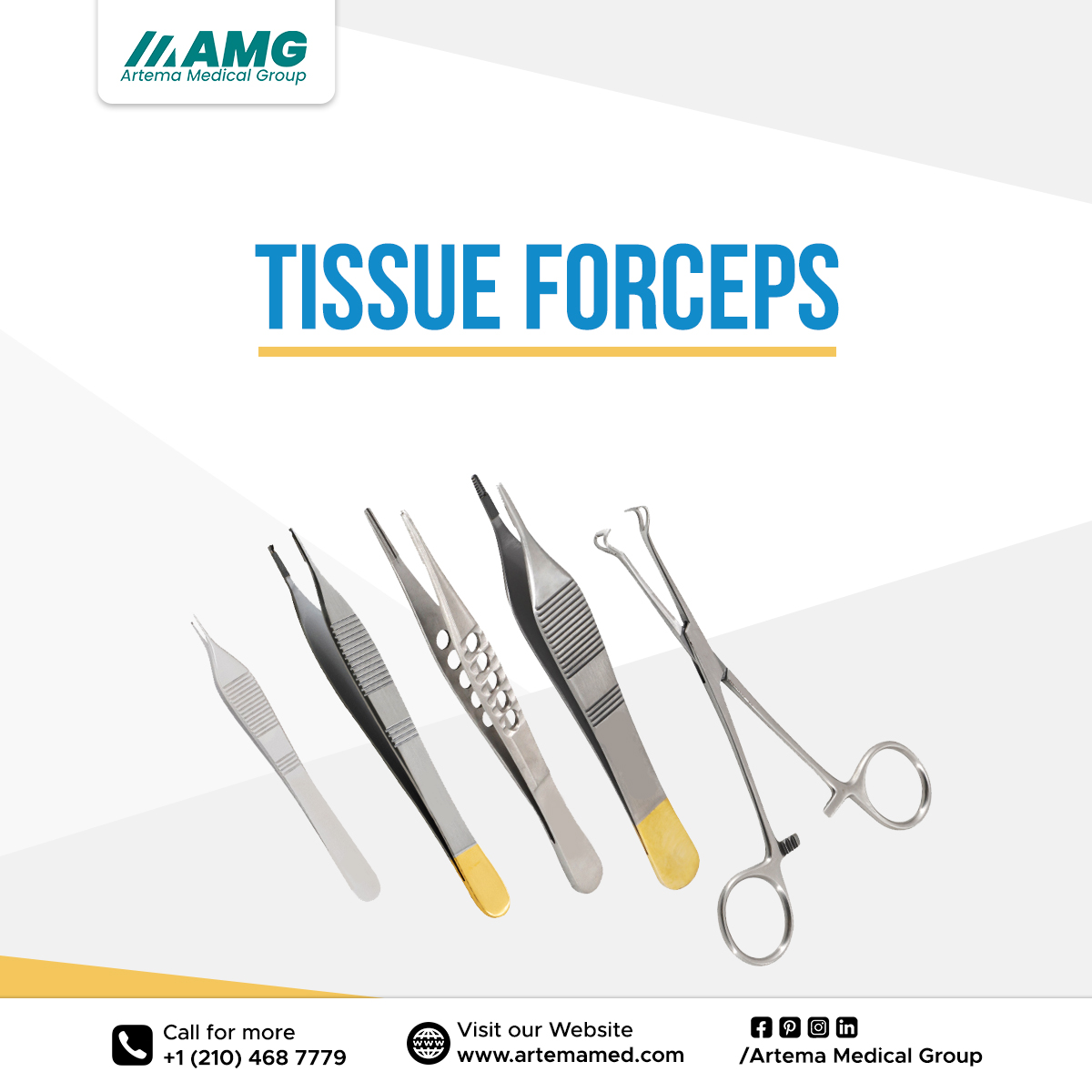
The Difference of Tissue and Dressing Forceps
Surgical forceps or surgical tweezers are mutual surgical instruments, but there’s a great variety of tweezers to take from. In general forceps can be congregated as browse through forceps (frequently called surgical tweezers, enthralling forceps, non-locking forceps or restraining forceps) or ring forceps (also called hemostats, hemostatic forceps and locking forceps). They are non-ratchet style. Focusing on skim forceps, they can be additional categorized as tissue forceps and dressing forceps. Let’s discover the differences between tissue forceps and dressing forceps for medical applications and investigation laboratories.
Tissue Forceps
Tissue forceps are used to hold and operate delicate tissues throughout surgical events or laboratory work. Their well tip is usually with small fangs or serrations and give them a good hold of the tissue devoid of inflicting harm. Fanged tissue forceps provide a better tissue hold and this could be helpful in any case where the tissue is oily or difficult to grip. One of the tweezer tips has one projection and the other consumes two. The edges align so that the teeth fit collected for a solid hold. However, the tusks may cause some flesh damage. The teeth can hole or tear delicate tissue, or they could permission indentations or scripts on the tissue. The grasp may not be as secure, but serrated tips diminish the chance of tissue trauma. For gentle tissues, choose serrated tips.
Tissue forceps with 1×3 teeth drink one tooth on one land fill and two teeth on the added tip of the tweezers. These tweezers will have a well tip for delicate tissue operation, such as during ophthalmic operation or plastic surgery. Tissue forceps with 2×3, 3×4, or 4×5 teeth have additional teeth on the tips for a more safe grip on tissue. These shapes are commonly used for rougher tissue, such as during orthopedic surgery or when eliminating tumors. However, they may not be appropriate for delicate flesh manipulation. Tweezers with more fangs increase the risk of tissue damage.
Do you want to visit Char Dham? Char Dham Travel Agent is the best place to plan your Char Dham tour. You can book the tour from here.
Tissue forceps by teeth are commonly rummage-sale in procedures such as dental hospital, ophthalmic operation, and microsurgery, anywhere precision and switch are essential. They can also be useful in events where the tissue is threatening or fibrous, such as during partition or when removing tumors. Workroom researchers use tissue forceps in microdissection, which includes the precise isolation and elimination of specific tissues or lockups for further examination or manipulation. They can hold and operate delicate tissue structures, such as plasma vessels, nerves, or single cells, under a optical microscope. Other research requests for tissue forceps include sample preparation, flesh culture, and histology.
Dressing Forceps
In contrast, dressing forceps (also known as pickups) are medical instruments that are normally designed to hold or operate dressings or other resources during wound care or other medicinal procedures. They are branded by their extended, thin handles. or 4×5 teeth are teeth with more teeth at the tips to do a safer hold on the tissue. These are the shapes used in rougher tissue i.e. when performing orthopedic surgery or when the need to get rid of a tumor. Nevertheless they are not perhaps suitable in working on delicate flesh. When tweezers have more fangs, there is more possibility of tissue damage.
In dental hospital, ophthalmic operation, and microsurgery, among other practices where precision and switching are vital, the most common is tissue forceps by teeth; among purchases made in rummage sales. They also come in handy during those occasions where the tissue at hand is threatening/fibrous as it happens during partition or tumor removal. Tissue forceps are at workroom in microdissection which involves the isolation and eradication of certain tissues or lockups and their further studying or processing. They are able to manipulate such fragile structures of tissue e.g., plasma vessel, nerve cell or even an individual cell and work with optical microscope. Sample preparation, flesh culture and histology are other uses of tissue forceps which are sought in other researches.
Would you like to visit Indiar? A tour operator in India is the best place to plan your tour. You can book a tour from here.
Tissue Forceps
Tissue forceps at Surgical Holdings are intended for delicately handling and greedy delicate tissues during procedures. Brought about by accuracy, these forceps have sharp jagged ends that bite into tissues and engage without causing injury. They are made of high standard stainless steel which protects durability and uniformity in different medical applications. The project on ergonomics will present easy-to-hold features which will assist the doctors to sustain a stable grip during operations. The ergonomic project offers comfortable handling, aiding doctors in maintaining a steady grasp throughout procedures. Obtainable in different sizes and tip shapes, these forceps cater to diverse medical needs and guarantee best tissue manipulation, ornamental surgical precision and enduring care. Check out the range of tissue forceps they provide at Clinical Holdings, a well-established supplier of clinical products.
Understanding Hemostatic Forceps:Design, Types, and Uses in Surgery
Surgical forceps are medical instruments by means of a historic birthright. The word forceps is derived from the Latin word “Etimos,” meaning a couple of pincers or tweezers. To date, seven hunderd different classes and shapes of tongs consume been exposed. Forceps play a important role in easing surgical operations by wounding, dissecting, and withdrawing soft or dense tissues. Forceps are typically named after the experts who discovered them or based on their functionality. For example, Adson forceps, Devaney forceps, Tissue forceps, Hemostatic forceps, etc.
Types of surgical forceps:
Based on the availability of a barring mechanism, forceps are separated into two major groups:
Would you like to visit Haridwar? Travel agents in Haridwar are the best place to plan your trip. You can book your tour right here.
Hemostatic forceps:
A fastening or notch mechanism is present in these forceps, commonly referred to as hemostats, ring tongs, or locking forceps.
Thumb forceps:
They lack a barring mechanism and are also recognized as tweezers or holding forceps.
Types of Hemostatic Forceps:
Kelly Hemostatic forceps:
They are ergonomicahally calculated with short grooves at their tips and are mainly used for clamping huge vessels or substantial tissues.
Rochester Hemostats:
They look comparable to Kelly forceps but are varied and have teeth on their tips to rub on more pressure and range out to deeper areas.
Mosquito forceps:
They have short instructions used to clamp lesser vessels. Generally available in three types:
- Hartman Mosquito Forceps: They are small in length, sharp and fine, then have jagged jaws.
- Hartman Mosquito Hemostats: They are intended to clamp small and actual fine blood vessels or sutures.
- Halstead Mosquito Forceps: They are alike to Hartman Mosquito Forceps but are extensive and lighter in heaviness.
Allis Tissue Forceps:
These forceps are intended for tissue removal and have shrill teeth with a strong grip. They are the preferred high-quality for delicate actions to protect healthy cells from harm.
Crile Hemostats:
They are analogous in shape to Halsted Mosquito forceps but are larger.
Rochester-Oschner Forceps:
Heavier in weight with irregularities and a tooth at their tip, these forceps are intended to deal with large blood containers and heavy tissues. Also obtainable in two other forms:
- Rochester-Carmalt Forceps: These forceps are the medical practitioner first choice to clamp small tissues and blood vessels. They are large with longitudinal serrations and cross-hatching at the tip. Common designations may take account of stars and stripes.
- Rochester-Pean Forceps: Pean forceps are alike in design to Rochester-Carmalt forceps but with flat serrations. They are intended to clamp large tissues and vessels.
Conclusion:
Particularly, hemostat forceps are important in directing bleed and guarding issues and in increasing surgical precision. They are ergonomically designed in such a way that they minimise tissue trauma, permitting attachment of blood containers and reduce blood loss during the operation eventually resulting in safer surgical
treatment and improved patient recovery.
More info: Artema Medical